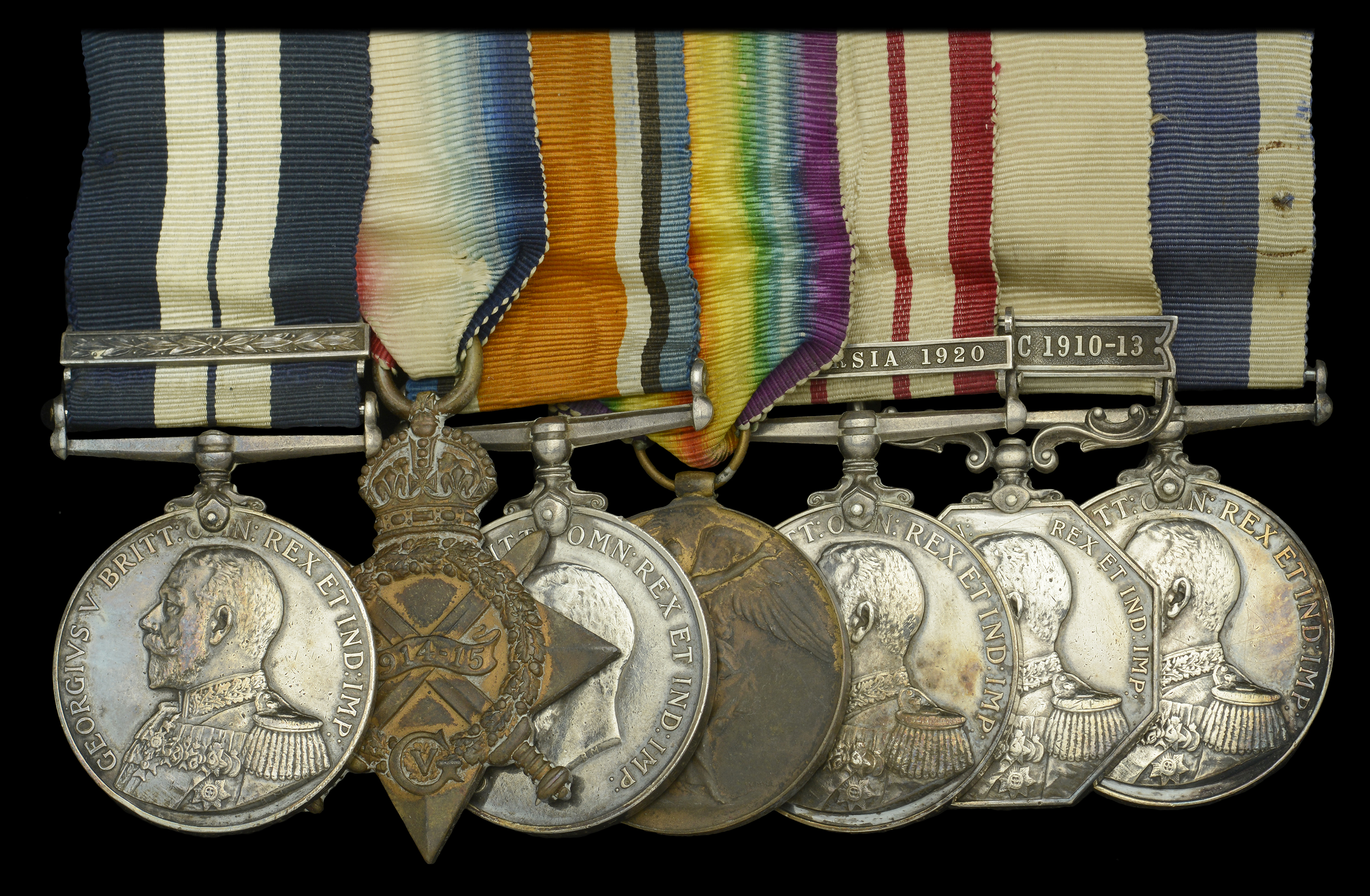
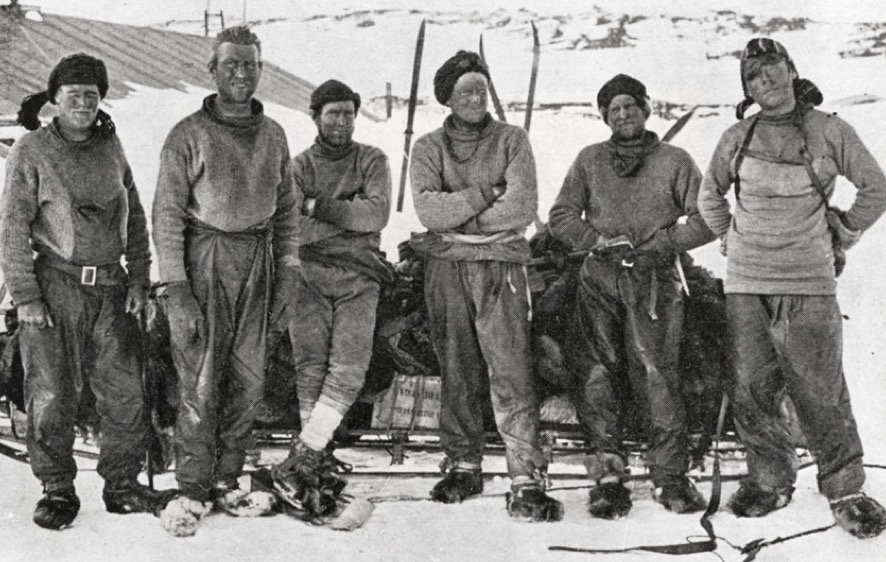
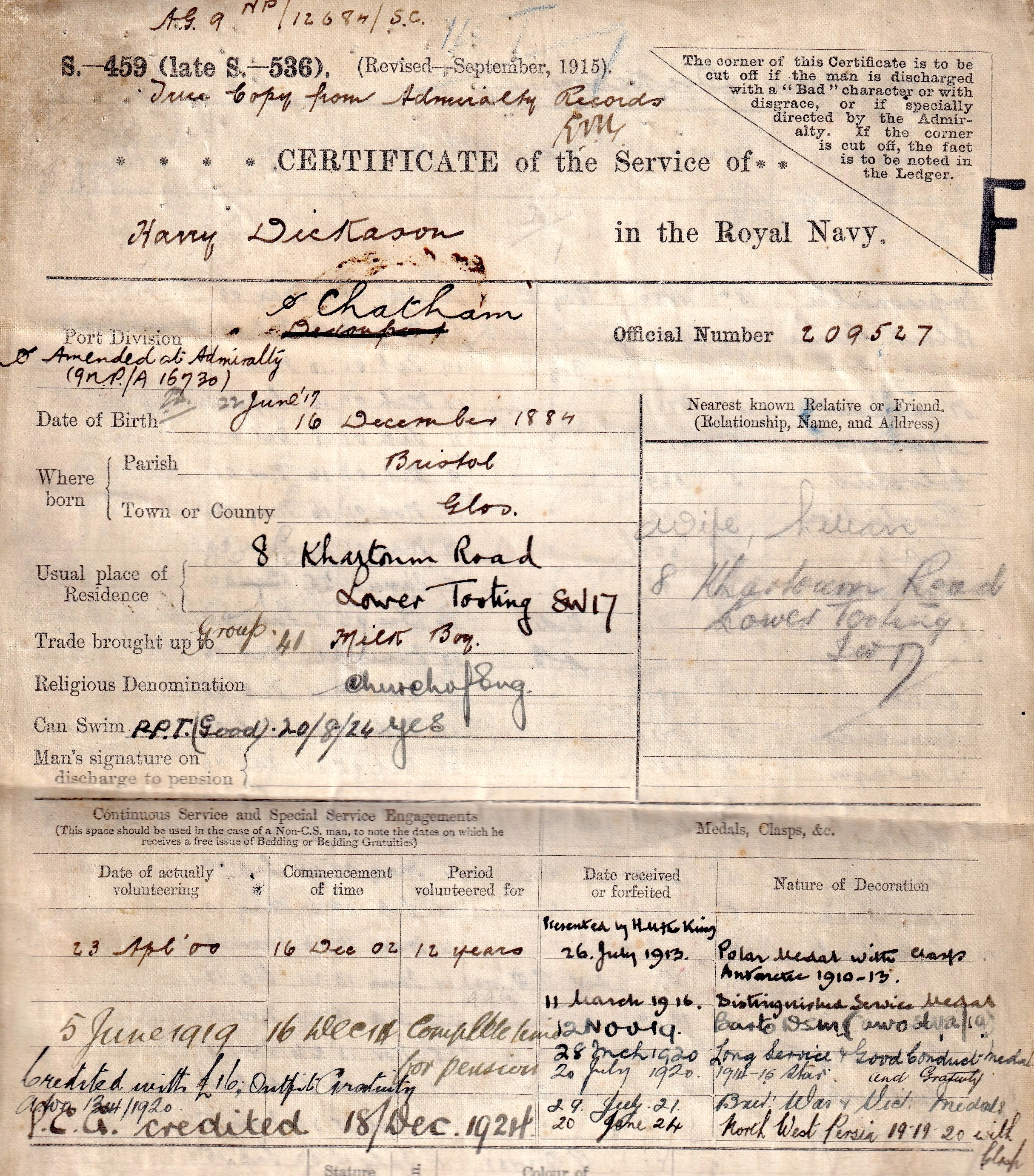
The unique and quite outstanding Great War Q-ship ‘Baralong incident’ D.S.M. and Caspian Sea 1919 operations Second Award Bar group of seven awarded to Chief Petty Officer Harry Dickason, Royal Navy, who had earlier been a stoic member of the Northern Party in Scott’s Antarctic Expedition of 1910-13, when, over nine months, he shared in a story of endurance and courage rarely matched in the annals of exploration. Afterwards an equally valued member of the North-West Persia Mission in 1920, when he became one of just four naval personnel awarded the related Medal and clasp ‘N.W. Persia 1920’ Distinguished Service Medal, G.V.R., with Second Award Bar (209527. H. Dickason, P.O. H.M.S. Baralong.) the reverse of the Bar officially impressed ‘Caspian Sea. 1918-19.’; 1914-15 Star (209527, H. Dickason. D.S.M., P.O., R.N.); British War and Victory Medals (209527 H. Dickason. P.O. R.N.); Naval General Service 1915-62, 1 clasp, N.W. Persia 1920 (209527 H. Dickason. C.P.O. R.N.); Polar Medal 1904, G.V.R., 1st issue, silver, 1 clasp, Antarctic 1910-13 (209527 H. Dickason, A.B. Terra Nova); Royal Navy L.S. & G.C., G.V.R., 1st issue (209527 Harry Dickason, P.O. H.M.S. Pembroke.) original mounting as worn, very fine or better and numismatically one of the most important Naval groups of the 20th Century (7) £50,000-£70,000 --- Importation Duty This lot is subject to importation duty of 5% on the hammer price unless exported outside the UK --- --- Just 67 Bars to the D.S.M. were awarded in the Great War. D.S.M. London Gazette 19 November 1915: ‘The following awards have been approved.’ The recommendation states: ‘H.M.S. Baralong. Sinking of German submarine U41 24 September 1915.’ One of two D.S.M.s awarded for this action. D.S.M. Second Award Bar London Gazette 11 November 1919: ‘To receive a Bar to the Distinguished Service Medal.’ The recommendation states: ‘H.M.S. Kruger. Caspian Sea 1918-19. Brought to notice for the work done on behalf of the expedition.’ Harry Dickason was born in Bristol, Gloucestershire on 16 December 1884, and worked as a milk boy prior to entering the Royal Navy as a Boy 2nd Class in April 1900. Advanced to Able Seaman in June 1904, he was serving in the battleship H.M.S. Montague when she was wrecked on Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel on 30 May 1906. In the summer of 1909, Dickason applied for a place in Scott’s second Antarctic Expedition, a successful application that saw him joining the Terra Nova in May 1910. Having then shared in the trials and tribulations of the Terra Nova’s stormy passage south, he served in the Northern Party, a six-man team under Commander Victor Campbell, R.N., between January 1911 and January 1913, a period that witnessed great danger and hardship. In addition to himself and Campbell, the party comprised Surgeon G. Murray Levick, R.N., the geologist Raymond Priestley, and Petty Officers G. P. Abbott and F. V. Browning. Having spent the first 10 months of their northern sojourn at Cape Adare, where several journeys of exploration were carried out and extensive scientific observations taken, Campbell and his team were embarked in the Terra Nova in January 1912 and proceeded to Evans Cove in Terra Nova Bay, where it was intended they carry out a six week expedition. As a result of adverse ice conditions, however, the Terra Nova was unable to come and pick them up, and Campbell and his men were left stranded, with few provisions, and the daunting prospect of the imminent arrival of the Polar winter: what followed over the next nine months was a story of endurance and courage rarely matched in the annals of exploration. Wearing summer clothing, and equipped with light tents, it was quickly apparent that if they were to survive more substantial shelter was required. To that end, the six-man team constructed a giant snow cave (or igloo), from which they rarely ventured, other than to hunt for seal and penguin. In company with Petty Officer Browning, Dickason designed a “blubber lamp”, without which the interior of the ice cave would have remained pitch black in the winter months; the lamp comprised a strand of rope suspended from a “bridge” across the top of a small Oxo tin filled with melted blubber. As recounted by Apsley Cherry-Garrard, in Worst Journey in the World, blubber was very much the Northern Party’s order of the day: ‘They ate blubber, cooked with blubber, had blubber lamps. Their clothes and gear were soaked with blubber, and the soot blackened them, their sleeping-bags, cookers, walls and roof, choked their throats and inflamed their eyes. Blubbery clothes are cold, and theirs were soon so torn as to afford little protection against the wind, and so stiff with blubber that they would stand up by themselves, in spite of frequent scrapings with knives and rubbings with penguin skins, and always there were underfoot the great granite boulders which made walking difficult even in daylight and calm weather … ’ Severe privations were suffered by all, Campbell recording in his journal cases of frostbite and dysentery, and ongoing hunger, the whole compounded by the low temperatures and extreme winds. Dickason was, at one stage or another, laid low by all these factors, in addition to suffering from snow blindness. In early August the sun returned, and the party prepared the sledges for the return to Cape Evans. Setting off on 30 September 1912, they reached Cape Roberts four weeks later, having in the interim come upon the welcome contents of an old depot left by Shackleton’s 1907-09 Nimrod expedition. In fact, they discovered yet further supplies at Cape Bernacchi and at Butter Point, discoveries that enabled their safe return to Hut Point on 6 November, but, here, of course, they learnt of the tragic fate of Scott and his party. A full account of the party’s experiences is to be found in team member Raymond Priestley’s Antarctic Adventure, Scott’s Northern Party, in addition to the aforementioned diary kept by Victor Campbell, which was published in Scott’s Last Expedition (Volume II). In his diary, Campbell makes frequent mention of Dickason, often in glowing terms. For his services to the expedition, he was advanced to Petty Officer and received his award of the Polar Medal from the King on 26 July 1913. Moreover, Mount Dickason, at the head of Boomerang Glacier in Victoria Land, is named after him. Dickason was serving ashore at Pembroke I on the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914, but, in typical fashion, he sought further adventure by volunteering for Q-ships in January 1915. Shortly afterwards he joined the Antwerp, the ex-G.E.R. passenger steamer Vienna, and only the second Q-ship to be commissioned by the Admiralty. He subsequently participated in the first Q-ship/U-boat encounter of the war, when, in March 1915, Antwerp went to the rescue of three merchantmen which had been sunk by the U-29. Although a bloodless encounter, it did persuade the Admiralty that smaller, less well-known ships were required if German U-boat commanders were going to be tempted into action. Accordingly, the Antwerp was relegated to transport duties and her guns transferred to the newly acquired tramp steamer Baralong. And with those guns went Dickason, who would shortly witness the destruction of two U-boats and the demise of half a dozen enemy submariners in circumstances that would attract allegations of war crimes. By the Spring of 1915, Baralong had been fitted out with three concealed 12-pounder guns, and one of her first notable acts was to race to the scene of the sinking of the L...